 |
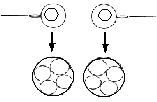
A twin pregnancy most commonly occurs when two separate eggs are fertilized by separate sperm to form two zygotes. Each zygote implants in the uterus individually and develops its own membranes and placenta. The two zygotes continue to develop as two separate embryos. These twins are referred to as dizygotic (commonly known as fraternal) twins. Fraternal twins account for about 70 % of naturally occurring twins in the United States [1].
Trizygotic triplets occur when three separate eggs are fertilized by three separate sperm.
| ||
 | Twins may also occur if a single fertilized egg forms a zygote that divides to form two separate embryos. These twins are referred to asmonozygotic or "identical" twins. Identical twins account for about 30% of naturally occurring twins in the United States [1] Monozygotic (identical) triplets may occur if a single fertilized egg forms a zygote that divides to form three separate embryos . | ||
Any combination of the above processes may occur in the creation of higher order pregnancies (triplets, quadruplets, etc.) . For example dizygotic triplets may develop from two separate eggs fertilized by separate sperm to form two zygotes. One of the zygotes then divides to form two separate embryos (as for monozygotic twins). Dr. Curran is a board-certified perinatologist with the San Gabriel Valley Perinatal Medical Group , Calif SUPERFECUNDATION
SUPERFETATION
Superfetation is the fertilization of two or more ova (eggs) during DIFFERENT menstrual cycles. This process is not thought to occur naturally in humans, but might occur using assisted reproductive technologies (ART). Superfetation is sometimes confused with superfecundation.[4]
THE "VANISHING" TWIN
There are more twins conceived than are born. Loss of a twin during the first trimester appears to be a relatively common occurrence [5-7] and is known as vanishing twin syndrome. The loss of one twin can be expected in about 40% of pregnancies identified with twin sacs or embryos [7].
Loss of one twin in the first trimester does not appear to impair the development of the surviving twin [8]. However, a deceased co-twin may cause an elevated amniotic fluid alpha-fetoprotein AFP and acetylcholinesterase (AChE) test result in an apparently normal surviving fetus [9, 10].
DIZYGOTIC (FRATERNAL) TWINS PLACENTAL TYPESDichorionic (two placentas), Diamniotic (two amnions) Dizygotic (fraternal) twins develop in two separate amniotic sacs (bag of water) and will have their own, separate, placentas. However, the placentas may at times appear to be fused. | |||
  LifeART image copyright 2005 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. All rights reserved. ULTRASOUND FINDINGS
| |||
FACTORS INFLUENCING THE OCCURRENCE OF DIZYGOTIC TWINS
"The probability of a subsequent twin pregnancy is increased 4-fold in mothers of twins, and the risk of having dizygotic twins is roughly doubled for women whose mother or sister has dizygotic twins " [18]. High follicular follicle-stimulating hormone level may explain the hereditary tendency for multiple ovulation and pregnancy in some families [19,20]. | |||
Other Pregnancy Term
<--Pregnancy Term Keywords --> Pregnancy Abdomen,The Belly,Abdominal circumference (AC),Abortion,Abruptio placenta (Placental abruption),Acceleration,Acromelia,Active Labor,Acute Cervical Insufficiency,Afterbirth,Agenesis of the corpus callosum (ACC),Akinesia,Alloimmunization (Isoimmunization),Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP),Amniocentesis,Amnioinfusion,Amniotic fluid,Amniotic Fluid Index (AFI),Amniotic fluid ‘sludge’,Amniotic sac,Amniotic sheet,Amniotomy (artificial rupture of membranes , AROM),pregnancy terms,elifexpert,Anemia,Anencephaly,Anesthesia,Angle of insonation,Anomaly,Antenatal,Antenatal corticosteroids , ACS,Antepartum,Anterior,Antibody (Immunoglobulin),Anticardiolipin antibodies (ACA, aCL Antibody) *,Anti-c antibody (little c antibody) *,Anti-D antibody (Rh sensitization, Rh disease)*,Anti-Duffy antibody (anti-Fya antibody),Anti-Kell antibody,Anti-Kidd antibody (anti-Jka or anti-Jkb),Anti-Lewis antibody,Anti-S antibody,Apgar Score


No comments: